Safeguarding Food Safety: Understanding Pesticide Residual Content and International Regulations

Revolutionizing the Culinary Landscape: Exploring Modern Food Technology
July 13, 2023
Pioneering a Sustainable Future: Exploring the Promising Path of Lab-Grown Meat
July 13, 2023Introduction:
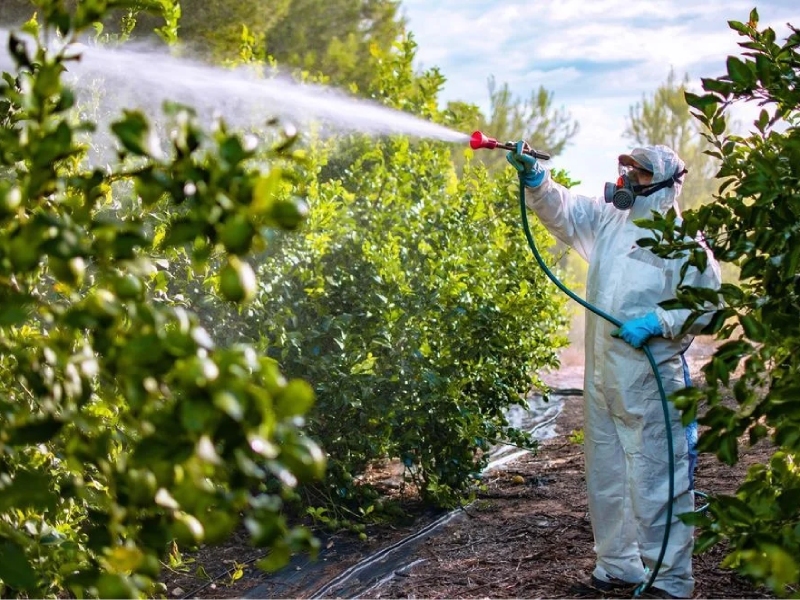
Ensuring the safety of our food supply is of paramount importance. Pesticides, commonly used in agriculture to protect crops from pests and diseases, play a significant role in food production. However, concerns have been raised about the potential health risks associated with pesticide residues in food. In response, international regulations have been established to monitor and regulate pesticide usage, setting maximum residue limits (MRLs) to protect consumer health. This blog explores the topic of pesticide residual content, its impact on food safety, and the international regulations that govern it.
- Pesticide Residual Content: Understanding the Basics
Pesticide residual content refers to the presence of pesticide residues in food products after their application during the growing or processing stages. Pesticides can enter the food chain through various pathways, including soil, water, and air. These residues can persist in food and pose potential health risks if consumed above acceptable levels. It is crucial to note that not all pesticide residues are harmful, as MRLs are set based on extensive scientific research to establish safe exposure levels for consumers.
- International Regulations and Maximum Residue Limits (MRLs)
To ensure food safety and protect consumer health, international organizations, such as the Codex Alimentarius Commission, the European Union, and the United States Food and Drug Administration, have established regulations and MRLs for pesticides. MRLs specify the maximum allowable concentration of pesticide residues in food products. They are based on scientific assessments that consider factors such as toxicity, exposure, and dietary habits. These regulations enable governments and regulatory bodies to monitor and enforce compliance across the food supply chain, from farm to fork.
- Harmonization and Trade Considerations
Harmonization of pesticide regulations and MRLs is a critical aspect of international trade. Varying regulations across countries can create barriers to trade and complicate global food supply chains. Harmonization efforts aim to align regulations and establish common standards, facilitating trade while ensuring food safety. Organizations such as the World Trade Organization (WTO) and the International Plant Protection Convention (IPPC) work towards harmonizing regulations to streamline international trade in agricultural products.
- Analytical Techniques and Monitoring Programs
To enforce compliance with MRLs, robust analytical techniques are employed to detect and measure pesticide residues in food products. Sophisticated laboratory methods, such as gas chromatography and mass spectrometry, enable accurate quantification of residue levels. Governments, regulatory bodies, and food industry stakeholders implement monitoring programs to routinely sample and analyze food products for pesticide residues. Non-compliant products are flagged, and appropriate actions are taken to ensure food safety.
Conclusion
Pesticide residual content in food products is a crucial consideration for ensuring food safety and protecting consumer health. International regulations and MRLs play a vital role in monitoring and controlling pesticide usage, with the aim of establishing safe exposure levels. Harmonization efforts and trade considerations help facilitate global trade in agricultural products while maintaining food safety standards. Robust analytical techniques and monitoring programs enable the detection and control of pesticide residues in food products. By staying informed about pesticide regulations and supporting global efforts, we contribute to a safer and healthier food supply chain, fostering consumer confidence and well-being.